1.The structure of the packed tower and the performance of the packed tower
2. Hydrodynamic performance of packed tower
3. Accessories for packed tower
Packing tower structure and packing performance
Introduction to Packed Tower
- Packed towers first appeared in the middle of the nineteenth century, used for distillation operations in 1881, and were introduced into the oil refining industry in the early twentieth century.
- Packed tower is one of the most commonly used vapor-liquid mass transfer equipment. It is widely used in distillation, absorption, desorption, stripping, extraction, chemical exchange, washing and heat exchange processes.
Packing tower structure
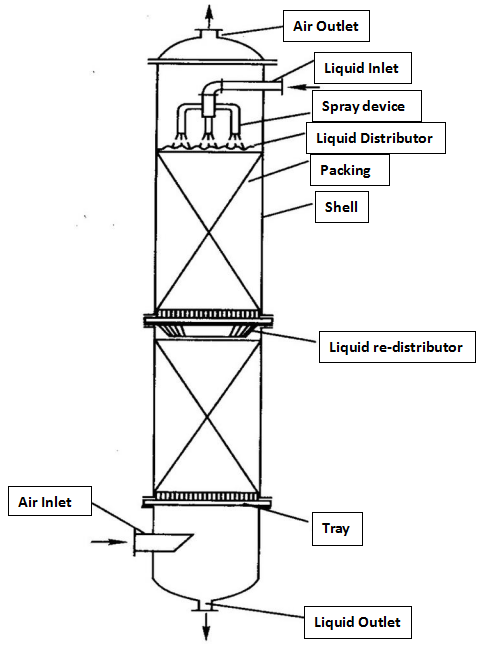

2. Packed tower operation
(1) The operation principle of packed tower
A. The liquid is sprayed onto the packing from the top of the tower through the liquid distributor, and flows down the surface of the packing;
B. The vapor is fed in from the bottom of the tower by the vapor distribution device, it continuously passes through the gap of the packing layer in counter direction with the liquid;
C. On the surface of the packing, vapor-liquid two-phase contact for mass transfer.
(2) Operating characteristics of packed tower
A. The packed tower is a differential contact of vapor-liquid mass transfer equipment, and the two-phase composition changes continuously along the tower height;
B. Under normal operating conditions, the vapor phase is the continuous phase and the liquid phase is the dispersed phase.
3. The function of packing
Packing plays an important role in the operation of packed towers.
Mainly:
A. Wetting the surface of the packing by liquid to increases the vapor-liquid contact area;
B. Extend the time of vapor-liquid contact;
C. The porosity of the packing layer not only promotes the uniform distribution of the air flow, but also promotes the turbulence of the vapor phase which increases the total mass transfer coefficient of the transfer process.
Materials of packing: carbon steel, stainless steel, ceramics, polymer materials (such as plastics), etc.